Install TimescaleDB on an existing PostgreSQL container
Table of Contents
- Introducing
- Installation
- Summary
Introducing
I have been conducting extensive research on TimescaleDB, a powerful relational database that is designed to handle time-series data. As part of my research, I recently encountered a challenge when trying to install TimescaleDB on an existing container. Despite initially struggling, I spent a considerable amount of time experimenting with different installation methods and configurations, and ultimately, I was able to successfully install TimescaleDB on my container.
Installation
We have an existing Postgres container with resources that we cannot override, such as our databases, and installed extensions. Since we cannot use sudo on the docker terminal and some packages required for TimescaleDB installation are missing, I customized the installation process. Here are the steps I took:
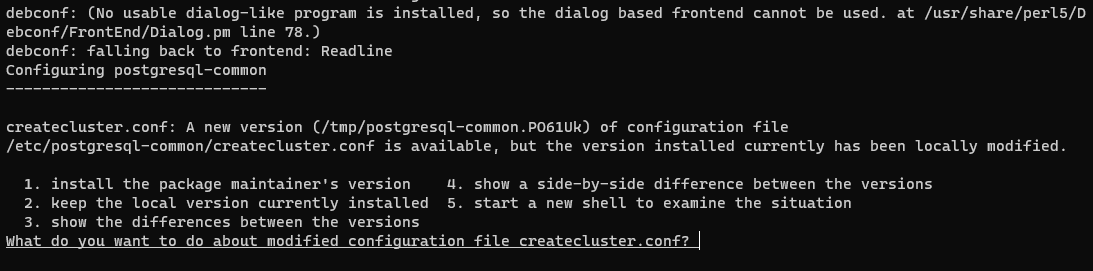
1. Install missing packages for docker container
apt-get update
apt-get install gnupg postgresql-common apt-transport-https lsb-base lsb-release wgetYou may receive a notification, in which case you can choose to install the package maintainer’s version by selecting 1 from the options. While it is not entirely clear what this option does, I tried it and it worked :)
2. Install TimescaleDB
- Add the TimescaleDB third party repository:
echo "deb https://packagecloud.io/timescale/timescaledb/debian/ $(lsb_release -c -s) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/timescaledb.list- Install Timescale GPG key:
wget --quiet -O - https://packagecloud.io/timescale/timescaledb/gpgkey | apt-key add -- Update your local repository list and install TimescaleDB:
apt-get update #Make sure your apt repository is up to date:
apt install timescaledb-2-postgresql-13 # based on PG version
apt-get install postgresql-client-13
apt-get update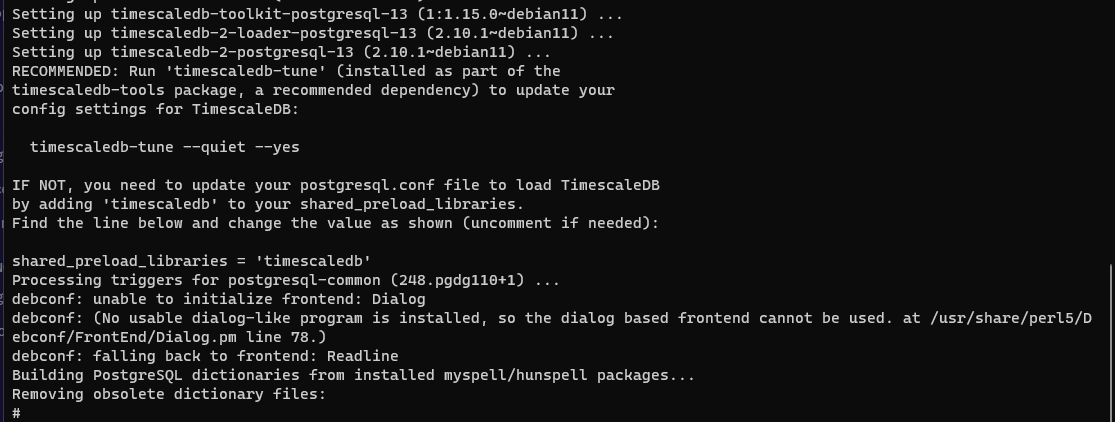
3. Update config settings for TimescaleDB
In this step, you need to add TimescaleDB to shared_preload_libraries. To avoid overriding current shared_preload_libraries settings, follow these steps to edit them:
- To display the
shared_preload_librariessettings in a container terminal, first log in to psql.
psql -U postgres -h localhost- Run this command:
show shared_preload_libraries;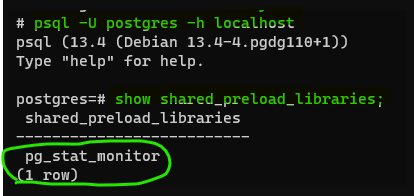
- I have previously added
pg_stat_monitor, so I need to expand my preload libraries:
ALTER SYSTEM SET shared_preload_libraries ='timescaledb','pg_stat_monitor';4. Now, you need to restart your Docker container to load TimescaleDB.
5. Add TimescaleDB extension
- Log in to psql again:
psql -U postgres -h localhost- Create a new database or switch to an existing one.
CREATE database tsdb;
\c tsdb # switching to tsdb - Create the TimescaleDB extension.
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS timescaledb;- Here are our results:
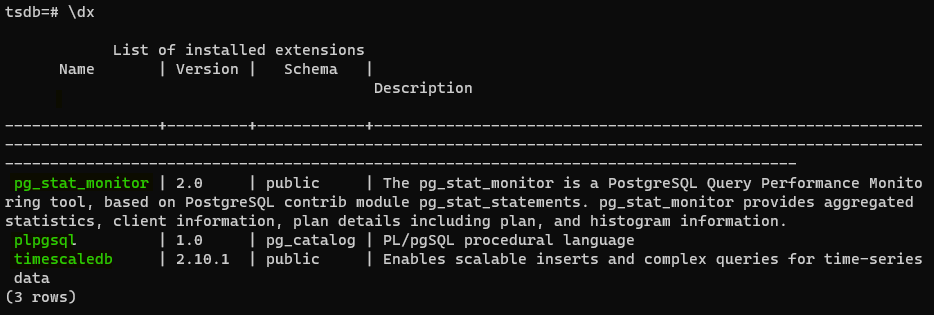
- Check that the TimescaleDB extension is installed by using the
\dxcommand at thepsqlprompt:
Summary
By following these steps, you can successfully set up TimescaleDB for time-series data in your PostgreSQL container. Finally, you can start ingesting time-series data into your PostgreSQL container using TimescaleDB’s specialized functions and operators. This allows you to analyze and visualize your data in new and exciting ways. I hope this article is helpful for you.

